Of mice and men; accounting for the latest (2018) observation that the same
cancers are found in man and animals (mice and rats) each cancer type being associated
with very specific frequencies and modulation schemes of mobile phone telephony, by Dr Chris Barnes, Bangor Scientific and
Educational Consultants e-mail Chris@bsec-wales.co.uk April 2018
Main site http://drchrisbarnes.co.uk
Important
Caveat: The IPR harmonics calculated in
this paper are for a GMF of some 48 micro-Tesla the approximate GMF in the UK
and Japan. I intend to address the
effects of GMF on a number of World Cancer distributions in some future
publications. I also intend to fully
account for the effects of Tumour Treating Fields in some future papers.
Abstract
The paper seeks to account
for the latest (2018) US Department of Health NTP observation (rodent study) that the same
cancers are found in man and animals (mice and rats) each cancer type being
associated with very specific frequencies and modulation schemes of mobile
phone telephony. The author’s previous
hypothesis of Ion Parametric Resonance in quantum coherence with cellular
soliton modes is further developed by considering specific ion channels
relevant to specific cancers. According
to the NTP study the rodent cancers
associated with GSM are Glioma, Prostate and Pancreatic. The present author has also shown some
association in the North Wales and in the human epidemiological model with GSM
and glioma and others have shown association of GSM with prostate cancer in
humans. According to the author’s hypothesis the ion channels disturbed by GSM
frequencies are the voltage gated chloride channel and the voltage gated sodium
channel. The data of Bennett et al (2004) suggest that
increased voltage-gated sodium channel expression alone is necessary and
sufficient to increase the invasive potential of a set of human prostate cancer
cell lines that serve as a model for prostate cancer metastasis. On the other
hand, the mechanism of 1900 CDMA is
common to both liver and lung cancer and is a unique facet of both frequency components which can coincide
with TRPM 7, proton and sodium and potassium
IPR.. Far field effects on humans are
also considered in a very small pilot study of 31 cancer cases. The hypothesis
that RFR stimulation of cation IPR/soliton modes is either cancer causing or
cancer promoting is supported. Different
cation modes are associated with different cancers. The hypothesis that RFR stimulation of
certain voltage gated chloride channels and their associated soliton modes may
be anticancer, especially for lung cancer, and especially when applied for
short transient periods is also supported. The IPR ion/ soliton model of
interaction too justifies further investigation. RF and DC field can predict the IPR frequency
but there is no reason to suppose that the soliton mode in itself does not set
the genetic expression of or
shape and size of the
channel. The work on ion channels is
essentially a beginning, perhaps an oversimplification. This is hardly surprising given that many ion
channels encoding genes have ‘superfamilies’(ref). No fewer than 10 genes encode for sodium, 16 for potassium and a staggering
100 for potassium. This probably
explains the observation of common and personal tumour treating frequencies as
mentioned by Zimmermann et al
(20120> https://www.nature.com/articles/bjc2011523There
is scope for considerable further work which could potentially be of immense
benefit to human kind.
1. I propose getting cancer registries to
release as much data as possible to be used with a GIS study to fully validate
both the quantum and IPR/soliton hypotheses.
2. I propose that extensive laboratory
studies are needed to look into RF and modulation duty cycle effects on the
various phases of healthy and cancer cell cycles.
Only with such data
can we fully understand this enthralling subject and develop a truly
electromagnetic and drug free cancer medicine regime.
Introduction
It
has long been known that interactions of EMF and EMR with Biosystems appear to
be quantised in some way with regard to both frequency and field strength. This observation alone is sufficient to
account for the fact that some 40% of known studies prove a negative
association of any interaction or bioeffect per se. Negative studies have been used by some to
support the notion that EMF and EMR fields pose no threat to human health and
to suggest that somehow the results of positive studies or associations are
fundamentally flawed.
Until
very recently indeed there existed no adequate theory to fully explain the
observable effects, in particular the so-called frequency windowing
effect. The present author has provided
such theory (ref).
Moreover,
prior to the advent of mobile telephony most studies of the epidemiological
effects of EMF/ EMR on the general public were limited to those living within
the near field of power lines, the near
field of Medium Wave Broadcast Transmitters and the far field of TV and FM radio transmitters.
Out
of a significant number of studies the conclusions were that there was a
slightly increased risk of certain types of leukaemia (refs). One study suggested a slightly increased
risk of melanoma skin cancer and this has recently been elucidated in much
greater detail by others(refs).
One
group of individuals exposed to EMF/EMR at probable higher field strengths and
for more sustained times are professional and amateur radio operators. Milham
(1988) studied death records for a significant number of US Radio
Amateurs. Three cancers had excess odds
ratios which I have calculated from Milham’s data, these are namely; Lymphoma (NHL) ad Myeloma both odds ratio =2.8, Myeloid Leukaemia, odds ratio 1.41 and
Prostate Cancer odds ratio 1.15.
Another
similar study suggested a slight
increase in the risk of ALS (MND).
Radio
Amateurs are exposed to high levels of 50/60 Hz fields from the power
transformers associated with their equipment as well as to specific short wave
frequencies in the 1.8 -30 MHz range and some also use VHF and UHF frequencies.
Interestingly
the odds ratio I have calculated for Leukaemia is virtually the same as that
given by Coleman (1988) for electricity workers. Thus it could be argued that the 50/60 Hz
fields the radio hams are exposed to are a most significant factor.
Taking the very largest example of EMR in our
present radio frequency environment, namely mobile telephony and based solely
on incidences of Glioma brain cancer, has led to various classifications over
the years culminating in the 2011 W.H.O type 2b carcinogen classification. Group 2b: an agent is ‘possibly
carcinogenic to humans’. There is limited evidence in humans that it causes
cancer and the evidence from animal studies is ‘less than sufficient’. This is
the new classification for mobile phones. Cancer Research UK consider Group 2B
to mean that, ‘there is some evidence for a risk but it’s not that convincing’.
Lloyd-Morgan
(2015) reviews the epidemiology of glioma in adults with respect to mobile
phone use and comes to the conclusion that previous assumptions of lack of
association were, in fact, seriously flawed and require revision.
The
above results are suggest yet with no real certainty, that different
frequencies of EMF/EMR might either cause or promote different cancers.
Mobile
phone systems have developed rapidly since their general inception in the
1990’s. There is now a myriad of
operational frequencies and modulation techniques. Intuitively and in the light of frequency
windowing effects alone one would expect different types of mobile phone system
to cause different, if any, biological effect.
Part I : Near field effects
Ten
years of planning went into the ‘NPT’ study, a 25 million-dollar US Government
rodent study that proves RF radiation levels common to cell phone use can pose
a risk of certain cancers and if so which.
Essentially the rodents lived in
the near field of a transmitting antenna but only being exposed the RF levels
common to that of a mobile handset.
The
NTP study tested Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) modulated
exposures (AT&T and T-Mobile use GSM frequencies), concluding GSM
bioeffects on male rats were seen in the prostate gland and in pancreatic
islets, and granular cell tumours of the brain.
Such
effects were NOT observed in Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA)–modulated
-exposed rats (Sprint, Verizon, and US Cellular use CDMA frequencies).
Conversely,
liver effects were noted only in CDMA-exposed male rats.
Findings At 900 MHz: AT&T and
T-Mobile use GSM frequencies
Some evidence linking RFR with malignant schwannoma
in the hearts of male rats, no evidence for same in female rats. Equivocal
evidence linking exposure to malignant brain glioma in females. Other tumors of
various types in both sexes “may have been related to cell phone RFR
exposure,”. Less serious “nonneoplastic lesions” were more frequent in exposed
males and females.
Findings At 1900
MHz: Sprint, Verizon, and US Cellular use CDMA frequencies
Equivocal evidence of carcinogenicity in lung,
liver and other organ tissues in both male and female mice.
Otis Brawley, the chief medical officer of
the American Cancer Society said, “The
NTP report linking radiofrequency radiation to two types of cancer marks a paradigm shift in our
understanding of radiation and cancer risk,”
Thus
the NTP study establishes a relationship
between different exposure responses to GSM technology used by AT&T and
T-Mobile or CDMA technology used by Sprint, Verizon, and US Cellular. The NTP study supports evidence that the
frequency of radiation exposure is as important as the intensity of RF exposure
in differentiating potential health risk from one frequency of RF exposure over
another.
Trying
to find a control group of people not exposed to cell phone radiation sounds
impossible in today’s age. However, to
validate the results of the NTP rodent radiation study in human terms, we need
a group of people exposed to only CDMA radiation and cut off completely from the outside world’s GSM
frequencies.
Lucky
for us such a place exists and provides a natural human control group
supporting the rodent study claims that GSM and CDMA wireless technology target
different cells and organs. More data
proving that we are susceptible to different frequencies used by different
phone network carrier technologies ought also to raise a red flag for the rollout of new 5G
technology known as millimeter wave technology.
Most
of the world uses GSM to some extent, except for the island nation of Japan
wherein GSM technology was never deployed.
Vast distances over water isolate everyone in Japan from anything but
CDMA frequencies. GSM phones are simply of no use there.
The
NTP study showed male rats exposed to GSM frequencies had higher rates of
abnormal prostate cells, and if this is also true for humans then the
population of Japan without any exposure
to GSM frequencies should have prostate cancers at a much lower rate than other
developed countries that use GSM technology.
Japan
has the lowest instance rate of prostate cancers in the world – nearly 300%
lower than the USA. Prostate gland
effects were not observed in CDMA-exposed rats, and the entire population of
Japan has always used CDMA technology.
Likewise,
the NTP study found that CDMA frequencies caused liver damage whereas GSM did
not. By extrapolation from rodent to human model we would expect an uptick in
liver cancer in Japan compared to the rest of the world where CDMA is less
common, and what is found is that Japan has the highest rate of liver cancer in
any industrialized country.
Thus,
now not only do we have frequency specific bio-effect i.e. frequency windowing
but we also have for the first-time substantial evidence of frequency/organ
specific carcinogenesis or at the very least frequency/organ specific cancer
promotion seemingly equally pertinent to the rodent and human model.
The
remainder of this present publication will explain the above observations and
consider other what other frequency/organ specific examples of
carcinogenesis can be found from within
the author’s own work and within the scientific literature. A universal hypothesis in terms of
perturbation of relevant voltage gated ion channels will be tested and strong support found.
Explaining the NTP observations and
human mirror.
Geesink
and Meijer have recently suggested that cancer is promoted by electromagnetic
decoherence (ref). This is truly an
elegant and exquisite piece of work but as usual with physical models there are
sometimes as many questions as answers.
For example, when one feeds into their model the known Schumann
resonance frequencies, some 50% fall on the life stabilising bands and some 50%
on the destabilising bands. It is hard
to see why life should have developed in this way unless this directly drove
the morphogenic fields of evolution itself through DNA mutation. The
model can suggest which frequencies ought to promote cancer and which
frequencies ought to suppress it but cannot account for the fact that different
frequencies seem to promote different cancers.
The
present author has previously provided a new hypothesis developed by extending
the earlier work of Geesink (ref) and linking its frequency condensates scale
to both Schuman resonances and Ion Parametric resonance.
The
hypothesis was carefully formulated to
bring together Bose Einstein ( Frolich ) condensate ‘Geesink’ modes and Ion Parametric Resonance. The conclusion is that these key frequencies
work in concert with Schumann resonance to normalise biological systems at an
ideal DC magnetic field strength. The hypothesis enjoys strong support in a
number of directions. For example, the prediction that cancer incidences would
vary according to the earth’s background DC field is fulfilled. A number of healing frequencies are
fully explained in terms of the particular ion channel being disturbed
especially pertinent to cancer wherein cancer cells some ion channels are
overexpressed. Perturbation of very
specific ion channels also explains dangerous effects of RF on biology.
My
previous assessment was that activation of voltage gated chloride channels is biologically dangerous and
explains for the first time the
few sparse observations of RF at
harmonics of 455-457 Hz being classed
by others as genotoxic. I will discuss
this at length further with regard to cell cycle dependent applications, see
discussion and further work. Further it
provides another mechanism by which RF (EMR) can generate ROS. I also proposed
that if voltage gated magnesium channel TRPM7 was also modulated by excessive frequency
sources at harmonics of 320-374 Hz both
additional oxidative and nitrosative stresses occur and either initiation of cancer
could follow or highly likely promotion
of existing cancer will follow.
This could account for why certain cancer latency or reoccurrence
periods appear to be reducing.
Certainly ionising radiation has this effect for breast cancer, see
Nguyen et al (2011). Another great
success of the theory was to explain why the team of Zimmerman and Pasche were
able to use physiological heartbeat changes to define their so called ‘TTF’
tumour treating frequencies. The same
sorts of ion channels expressed in heart muscle and nerve fibres are also
expressed in many cancer cells but not so much normal non-excitable
tissue. The theory also explained, for
the first time Hallberg’s observations of FM radio antenna polarisation
and melanoma. Finally, regarding power
windowing, the limit of human sensitivity is of the order of 1 picotesla, i.e.
pretty much the same magnitude
as Schumann resonance.
Thus in seeking to explain the NTP observations and human mirror, I
further extend and employ the above hypothesis. GSM 900/1800 has been shown by the above
study to be associated with Glioma and Prostate cancer.
Whereas
1900 MHz CDMA has been shown to be associated with both Liver and Lung cancers
in both the rodent and human models.
All
that is necessary is firstly, to reduce each carrier frequency and any
modulation frequencies onto the acoustic scale by successive division by powers
of 2. Secondly to identify the ion
channels perturbed for each of the calculated frequencies. Finally, to check if there is equivalence
between the involvement or expression of these ion channels in the specific
cancers involved.
According
to the NTP study the rodent cancers
associated with GSM are Glioma, Prostate and Pancreatic. The present author has also shown some
association in the North Wales and in the human epidemiological model with GSM
and glioma and others have shown association of GSM with prostate cancer in
humans.
According
to the author’s hypothesis the ion
channels disturbed by GSM frequencies are the voltage gated chloride channel
and the voltage gated sodium channel.
Thus
a further and fitting test of the extended hypothesis is to enquire if and how
these channels are relevant to the three associated cancers.
Olsen
et al (2003) state that voltage-gated chloride channels have recently been
implicated as being important for cell proliferation and invasive cell
migration of primary brain tumors cells. In their study they provide several
lines of evidence that glioma Cl– currents are primarily mediated by ClC-2 and
ClC-3, two genes that belong to the ClC superfamily.
Glioblastoma
is the most common and aggressive primary malignant brain tumor. Voltage-gated
chloride channels have been identified as crucial regulators of glioma cell
migration and invasion by mediating cell shape and volume change. Chloride channel blockers have been shown to
be effective against glioma.
It
is proposed thus that the mechanism of GSM RF must be counter to blocking i.e.
enhaning the chloride channel.
ClC-3
is also expressed in Human Prostate Cancer Epithelial Cells see Lemonnier et al
(2004).
FXYD3
is overexpressed in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and influences pancreatic
cancer cell growth. FXYD3, a
transmembrane protein that acts as a chloride channel or chloride channel
regulator. I postulate thus that the
mechanism of GSM RFR in pancreatic cancer is to act synergistically with FXYD3
to further enhance chloride transport.
Thus
we have a common thread in all three cancers which is enhanced chloride channel
and transport. I have previously
discussed the chloride channel as a dangerous route through which RF EMR can
generate ROS.
I
next turn to the voltage gated sodium channel.
Schrey
(2002) has shown voltage-sensitive sodium channels appear to be an
electrophysiological hallmark of gliomas.
Further, their study gives clear
evidence for a differential expression of sodium channel subtypes in gliomas
and indicates a predominant expression of channels related to malignancy
grades. Sodium channel subtypes are: Nav1.1,
Nav1.2, Nav1.3, Nav1.4, Nav1.6, and Nax (Nav2.1) Nav1.6 however seemed to be almost absent in
gliomas.
Voltage‐gated
Na+ channel (VGSC) activity has also been implicated in prostate cancer (PC)
metastasis. Although VGSCs can occur as multiple‐subunit assemblies, the
α‐subunits (VGSCαs) alone can encode functional channels. Diss et al (2001) conclude that several
VGSCα genes and their splice variants are expressed similarly in both rat
and human PC cell lines. (2) Expression levels are much higher in the strongly
metastatic (MAT‐LyLu/PC‐3) cells. (3) Levels of SCN9A mRNA
specifically are predominant in MAT‐LyLu and PC‐3 cells; thus,
SCN9A is highly likely to be the main source of the functional VGSC detected,
see Prostate 48:165–178, 2001. © 2001 Wiley‐Liss, Inc.
Diss
(2005) show Na v 1.7, to be associated with strong metastatic potential in
prostate cancer.
Anderson
et al 2003 have showed voltage-gated sodium channel blockers to be cytostatic
inhibitors of the androgen-independent prostate cancer cell line PC-3.
Mycielska
(2003) also showed a contribution of functional voltage‐gated Na+ channel
expression to cell behaviours involved in the metastatic cascade in rat
prostate cancer.
Thus
the conclusion is here that GSM RFR enhances the channel or transport therein,
I a similar manner to the chloride channel above.
No
significant references can be found as to the expression of voltage gated
sodium channels in pancreatic cancer of humans or rodents. Thus the conclusion most supported is that
only the chloride channel is disturbed by GSM RFR in the case of pancreatic
cancer whereas both the chloride and the sodium channel are disturbed in
gliomas and prostate cancer.
Glioma
was the most abundant cancer observed in the rodent study.
I
next turn to the effects of Verizon 1900 CDMA. The basic carrier frequency of 1900 MHz
reduces to 452 Hz on the Geesink Scale and the modulation effectively has a
spread comb like quasi random spectrum
from 2-16 Hz. Thus the ion channels
expected to be perturbed are the hydrogen ( proton) channel ( 452Hz ) and the sodium channel (256Hz ) and the
potassium channel ( 320 Hz) and the
TRPM 7 channel (320-374 Hz).
The
cancers observed are Liver and Lung in the rodent model and in Japan where 1900
CDMA has been exclusively used Liver cancer rates are very high and Lung cancer
rates are comparable with other parts of the world.
I
next seek to confirm the involvement of the hydrogen and sodium channel and TRPM 7 in these two cancers.
Over
activity of the proton channel HV1 increases proliferation in all types of
cancer cells, see Hong et al (2014).
Fang et al ( 2013) have showed that inhibiting the TRPM 7 channel stops
proliferation in rat liver cancer.
Since
1900 CDMA produces TRPM 7 IPR and soliton mode interaction it is not surprising
it is involved in proliferation of rat liver cancer. Gao et al (2011) describes TRPM7 as a
potential target for lung cancer treatment.
Spugninni
et al (2015) conclude:
• pH derangement is a common feature of
cancers.
·
Major determinants of aberrant pH gradient
in cancer are proton exchangers and transporters.
·
These include V-ATPase, Na+/H+ exchanger,
MC transporters, CA.
·
Through proton transporters and exchangers
tumors isolate themselves from the body.
·
Pharmacological inhibition of these molecules
may represent the future of cancer therapy.
Proton
channels may be considered as a class of Acid Sensing Channel or ASICS. An acidic microenvironment promotes carcinoma
cell proliferation and migration. Acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs) are H+, Ca2+,
and Na+-gated cation channels that are activated by changes in the
extracellular pH, and ASIC1α may be associated with tumor proliferation
and migration.
Jin
et al (2015) investigated the role of
ASIC1α in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) migration and invasion. The
expression of ASIC1α was examined in 15 paired HCC and adjacent non-tumor
tissues by immunohistochemistry. A
moderately acidic extracellular environment promoted ASIC1α expression,
and silencing of ASIC1α expression inhibited the migration and invasion of
HCC cells. Suppression of ASIC1α expression by RNAi attenuated the
malignant phenotype of HCC cells, suggesting a novel approach for anticancer
gene therapy.
Since
ASICS can also be activated by Sodium it is not surprising that 1900 CDMA causes
such a rise in HCC.
Furthermore
according to Yang et al (2011) Na+/H+
exchanger 1 gene (NHE1) expression was increased in HCC tissues and cells in
which its expression was associated with the increased tumour size, venous
invasion and advanced tumour stages.
Finally,
I turn to Potassium channels. Blockage of voltage-gated K+ channels inhibits adhesion
and proliferation of hepatocarcinomatous cells, see Zhou et al 2003. Thus I would propose that RFR stimulation of
IPR does the opposite and encourages proliferation.
Since
1900 CDMA has the potential to cause IPR of proton, sodium and potassium it is not surprising that associations are
found.
The
experiments of Roger et al (2007) suggest that the functional expression of
voltage-gated sodium channels might be an integral component of the metastatic
process in non-small-cell lung cancer cells probably through its involvement in
the regulation of intracellular sodium homeostasis. These channels could serve
both as novel markers of the metastatic phenotype and as potential new
therapeutic targets.
Similar
to the work of Yang above, Li et al (2009) has also showed that inhibition of
proliferation and apoptosis in drug-resistant human small cell lung cancer
cells may be induced by a Na+/H+ exchanger-1 (NHE-1) antisense gene.
Finally,
I consider the potassium channel and lung cancer. Anti-proliferative effect of Kv1.3 blockers
in A549 human lung adenocarcinoma in vitro and in vivo have been studied by Jang et al (2010). In their study, they investigated the effects of
suppression of Kv1.3 expression on cell proliferation and cell cycle
progression in human lung adenocarcinoma, A549 cells. Treatment with margatoxin
(MgTX), a selective blocker of Kv1.3 or short hairpin RNA (shRNA) against Kv1.3,
significantly blocked A549 cells' proliferation. In addition, selective
inhibition of Kv1.3 significantly increased expression level of p21Waf1/Cip1
and significantly decreased the expression level of Cdk4 and cyclin D3. They also applied the MgTX into a xenograft model
using nude mice, and MgTX caused a reduction of tumor volume when it was
injected into the tumor tissues. Their results suggest that Kv1.3 may serve as a
novel therapeutic target for lung adenocarcinoma therapy.
I
thus propose that the mechanism of 1900 CDMA is common to both liver and lung
cancer and is a unique facet of both
frequency components which can coincide with TRPM 7, proton and sodium and potassium IPR.
Explaining some of the previous near
field observations.
1.
Leukaemia
in power workers
50/60 Hz are sufficiently close to stimulate sodium and magnesium IPR normally under the
control of the 1st Schumann mode.
IPR
is expected with 50Hz at the Sodium Channel and with 60 Hz at the Proton
channel Hv1.
Enhancement
of Voltage-gated Na+ Channel Current is Associated with Multidrug Resistance in
Human Leukemia Cells, Yamashita et al
(1987).
Endogenously
expressed Mg2+‐dependent cation channels in K562 cells and the MIC
channels in other hematopoietic cells might be formed by different channel
proteins, see Semenova et al (2005).
The
voltage-gated proton channel, H V 1, has been implicated in numerous biological
functions diseases such as ischemic stroke, breast cancer, and chronic
lymphocytic leukemia, see Dudev et al 2015.
Petheo
et al (2010) detected a significant
amount of Hv1 in human eosinophil and neutrophil granulocytes and in PLB-985
leukaemia cells. Using RNA
interference, they obtained strong correlation between Hv1 expression and IHv
density in PLB-985 cells. It was also demonstrated that a massive reduction in
Hv1 expression can limit the Nox2 mediated superoxide production of PLB-985
granulocytes.
2.
Leukaemia
in Radio Amateurs
The
study of Milham was of US Radio Amateurs thus the 60 Hz IPR as above will be relevant. Hence proton IPR will be highly
relevant. Different chloride channels
are also expressed in leukemic and normal cells see Jiang (2002). Coincidentally most of the frequencies that
radio amateurs use would coincide with chloride frequencies or about 433 Hz on
the Geesink scale. It is doubtful if
actual transmission periods will be relevant.
Most radio hams spend more time listening than transmitting but they do
spend a lot of time sitting near power supplies which will be emitting 60 Hz
fields. I postulate that continuous
radio frequency emissions from mobile phone base stations, pagers, TETRA and
Commercial Radio and TV transmitters could be potentially far more
hazardous than the short bursts of emission from a Ham Radio Station which do
not last for significant durations of the cell cycle.
Summary of Results
The results are most elegantly
summarised in Table form.
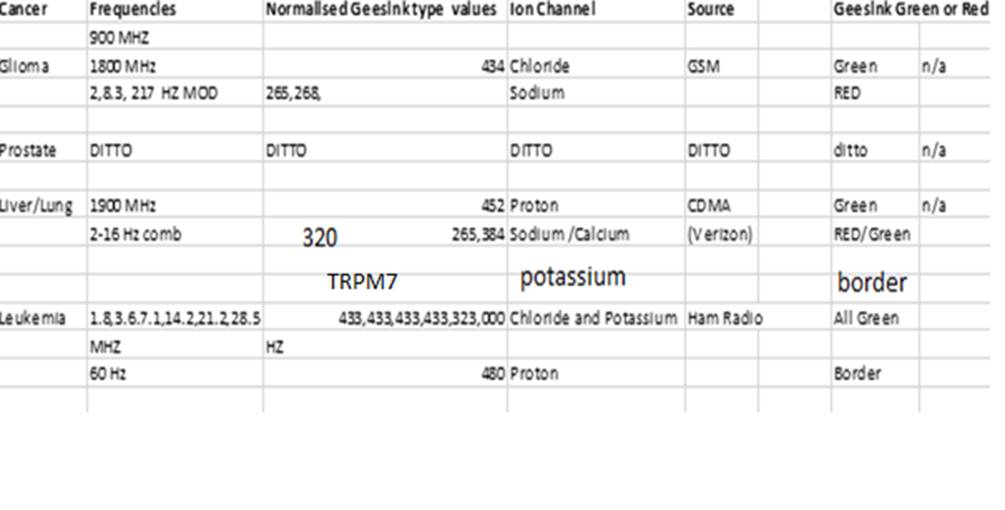
Table 1
Further Discussion
Reference
has been made above to the work of Geesink and Meijer ( refs). In their latest (2018) work they make
reference to over 200 individual studies of EMF and RFR on living systems and
evaluate the results according to
factors such as carrier frequency, modulation frequency and bandwidth. Carrier frequencies which are narrow and
pure i.e. little or no phase noise and fall on the stabilising frequencies of
the condensate produce either no or advantageous biological effect. Those which fall on the dephasing or
decohering (anti-condensate) frequencies seem to be associated with cancer
initiation or proliferation. Even those
which fall on the stabilising frequencies have destabilisation effects if they
have either modulation frequencies which fall in any of the destabilising zones
and/or modulation bandwidth which exceeds ….% of the carrier frequency.
1.
Effects
of GSM man and rodents
It
is logical therefore to attempt to retrospectively apply the Geesink model to
the present results as a reinforcing test.
Referring then to Table 1 in the case of Glioma induced by GSM only the
modulating frequencies lie in the ‘red’ destabilising zone and these are they
which stimulate Sodium IPR. I would
expect to find evidence of sodium channel blockers inhibiting glioma if the contrary is true and Sodium IPR
by RFR is a promoter.
Smitherman
and Sontheimer (2001) shoed the inhibition of Glial Na+ and K+ Currents by
Tamoxifen (tmx) . Incubation with tmx significantly was seen to reduce cell
proliferation as examined by 3[H]-thymidine uptake.
Kappor
et al (2009) showed that knockdown of ASIC1 and Epithelial Sodium Channel
Subunits Inhibits Glioblastoma Whole Cell Current and Cell Migration.
The
above evidence fits exactly with my expectations.
Further
I would expect the sodium channel to be
equally relevant to prostate cancer.
Hoosein
(2002) considered voltage-gated sodium ion channels in prostate cancer (Pca)
both in terms of expression and
activity. Their results indicated increased expression of
VGSCs in Pca and VGSC involvement in Pca growth.
Anderson
et al (2003) examined voltage-gated sodium channel blockers as cytostatic
inhibitors of the androgen-independent prostate cancer cell line PC-3. Hydroxyamides and a hydantoin were found to be effective.
Hoosein
(2001) showed that Phenytoin and carbamazepine, which inactivate voltage-gated
sodium channels, inhibited the secretion of PSA by LNCaP and IL-6 by DU-145 and
PC-3 cell lines.
The
data of Bennett et al (2004) suggest
that increased voltage-gated sodium channel expression alone is necessary and sufficient to increase the invasive
potential of a set of human prostate cancer cell lines that serve as a model
for prostate cancer metastasis.
One
again the above results exactly vindicate
my hypothesis.
2.
Effects
of Verizon CDMA man and rodents: lung and liver cancers
The
modulation frequencies suggest that both sodium and potassium could be relevant
in the promotion of both lung and liver cancer by CDMA. Intuitively
there has to potassium involvement else I would have expected GSM to produce
these same cancers.
To
reiterate, the anti-proliferative effect of Kv1.3 blockers in A549 human lung
adenocarcinoma in vitro and in vivo have
been studied by Jang et al (2010). In their
study, they investigated the effects of suppression of Kv1.3 expression
on cell proliferation and cell cycle progression in human lung adenocarcinoma,
A549 cells. Treatment with margatoxin (MgTX), a selective blocker of Kv1.3 or
short hairpin RNA (shRNA) against Kv1.3, significantly blocked A549 cells'
proliferation. In addition, selective inhibition of Kv1.3 significantly
increased expression level of p21Waf1/Cip1 and significantly decreased the
expression level of Cdk4 and cyclin D3.
They also applied the MgTX into a
xenograft model using nude mice, and MgTX caused a reduction of tumor volume
when it was injected into the tumor tissues. Their results suggest that Kv1.3 may serve as a
novel therapeutic target for lung adenocarcinoma therapy.
Blockage
of voltage-gated K+ channels inhibits adhesion and proliferation of
hepatocarcinomatous cells, see Zhou et al 2003.
Koch
and Leffert (1979) showed that increased sodium ion influx is necessary to
initiate rat hepatocyte proliferation.
Only
CDMA provides a mechanism for stimulating both the sodium and potassium
channels by IPR by means of its modulation.
Presently
insufficient evidence exists in the literature to comment with great certainly
on potassium on Lung Cancer but there is
evidence for TRPM7 on both lung and liver cancer.
Thus increased activity in TRPM7 alone is probably sufficient to account for
the association of Verizon CDMA
with lung and liver cancer.
3.
Leukaemia
60 Hz
Only
proton channel Hv1 ( approx. 480Hz) is stimulated. Asuage et al (2017) showed that
Diphenhydramine inhibits voltage-gated proton channels (Hv1) and induces
acidification in leukemic Jurkat T cells. Not only does this represent a potential new
pharmacological application and treatment for Leukaemia but it 100% supports my hypothesis.
Part II Far field effects.
So
far, I have dealt with laboratory studies, mobile phone handsets and the radio
ham station. All three exposed either
rodents or humans to near field conditions.
All
three sets of results elegantly support the present hypothesis that different
RF frequencies initiate or promote different cancers because of their coupling
to cellular soliton modes coincident with cancer specific ion channels or
groups of such channels.
Part
II of this work explores if this possibility also applies to far field signals
impinging with biology.
Although
there exist several public domain epidemiological studies of the effects of
Powerful MW Broadcasting stations, FM Broadcasting stations, TV Broadcasting
Stations and Mobile Phone Base stations the conclusions reached are very
mixed. Some suggest an increased risk of haemopoietic cancers such
as Leukaemia, NHL and Myelomas whilst others suggest increased risk of Brain
cancers and Breast and Prostate cancers. Some of the references are as
follows: Incidence of Cancer in the
Vicinity of Korean AM Radio TransmitterMina Ha , Hyung-Jun Lim , Soo-Hun Cho ,
Hyung-Do Choi & Kwang-Yun Cho
Pages
756-762 | Published online: 07 Aug 2010,
Cancer Incidence near Radio and Television Transmitters in Great Britain
I. Sutton Coldfield Transmitter
Helen
Dolk Gavin Shaddick Peter Walls Chris Grundy Bharat Thakrar Immo Kleinschmidt
Paul Elliott
American
Journal of Epidemiology, Volume 145, Issue 1, 1 January 1997, Pages 1–9, https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a009025, Electromagnetic radiation: Environmental
pollution and health
Anders
Ahlbom Maria Feychting
British
Medical Bulletin, Volume 68, Issue 1, 1 December 2003, Pages 157–165,
https://doi.org/10.1093/bmb/ldg030
Published:
01 December 2003,
Elmwood
(1999) makes the following
conclusion: ‘Several positive
associations suggesting an increased risk of some types of cancer in those who
may have had greater exposure to RF emissions have been reported. However, the
results are inconsistent: there is no type of cancer that has been consistently
associated with RF exposures.’
According
to my present hypothesis this is exactly the conclusion to be expected because
most commercial transmitting sites are multi-frequency installations and we
have seen above how, at least in the near field, different frequencies seem to promote
different cancers via the appropriate soliton/ion channel link.
Thus
if I am to elucidate further in this far field
analysis, I have no choice but to both employ some of my own locally
acquired experimental data and to rely
on anecdotal and press reports of cancer cases and deaths at various locations
and employ ‘site finder’ to see which frequencies are active at nearby
transmitters.
The
late Dr Neil Cherry (2002) was one of the first to realise that both the
spatial and temporal evolution of a signal emitted from either a TV or mobile
phone tower would be critical in determining related epidemiology https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/2848/19bae4232af253ec4073030e635172bedf32.pdf.
Following
Cherry and the arguments of Professor
Cyril Smith, a world renounced expert in magnetics, water memory and more
recently homeopathy, I re-analysed some
of the Dolk I and II data and found that the spatial distribution of biological
effects was not simply due to antenna lobe effects but rather had a quantum
mechanical origin.
This
additional piece of evidence facilitates my evaluation. The
observation I previously made was
that biological effects in the
far field of any transmitting antenna
follows a quantum mechanical frequency/distance rule based on the electromagnetic Aharonov–Bohm
effect. The same applies whether the
effect in question relates to bio-damage to trees ( ref) or to bio-damage to
humans.
Recently
it has been shown by van Vlaenderen (2001) that for electromagnetism the
generalised Maxwell equations also contain scalar field terms which predict the
existence of so called LES (longitudinal electro-scalar) waves in the vacuum
which have an associated power flow term. The experimental and theoretical work of Ziamidorogoa (2016) during solar
eclipses confirms van Vlaenderen. http://realstrannik.com/media/kunena/attachments/208/JMP_ElectroScalar_EnergyoftheSun(2).pdf Arbab (2014) also discusses ‘The modified
electromagnetism and the emergent longitudinal wave.’
Evans (2004) has stressed the possible
importance of the Electromagnetic Aharonov-Bohm effect in radar and signalling
technologies and is convinced that the effect is responsible for certain
effects of radio frequency radiation on animal and human physiology. I will endeavour to confirm this below.
Tomilin
(2013) discusses The Potential-Vortex Theory of Electromagnetic Waves and
explains the properties of the elctroscalar wave and the magnetic vector
potential. Concluding that there are
‘new opportunities for communications
technologies’.
Additionally,
if Batteaus’ (1968) hypothesis on nerve function proves correct, then the A –potential with its ability to perturb
electron wave function at a distance may be able to directly influence nerve
and brain tissue.
For
instance, and as first suggested by Smith http://cwl2004.powerwatch.org.uk/programme/posters/day4-smith.pdf
the electromagnetic radiation (E- and
B-fields) from a transmitter will experience refractive index and propagate at the velocity of light in air i.e. less than
that in the vacuum, but the magnetic vector potential-A (A-field), following
the Aharonov-Bohm effect, does not interact with matter (instead it alters the
phase of the electron wave-function) and so propagates at the vacuum velocity
of light. At 5 km distance from a 100 MHz VHF FM transmitter, there will thus
be a transit time difference of 5 ns between the A and B fields, based on
standard values for the dielectric constant and refractive index of air. At 100MHz, this distance or time delay
represents a 180º or pi/2 phase difference. I have expanded on this elsewhere
and have shown that the condition is also value for npi/2 when n is odd
(ref).
Smith
has suggested that frequency could be
imprinted into water alone, see https://hpathy.com/scientific-research/homeopathy-how-it-works-and-how-it-is-done-5/2/
or
that present such as living tissues.
Returning
to the analysis of Dolk, the frequency
band 70MHz-130MHz would cover the standard deviations in Smith’s data as
plotted. In the UK VHF FM broadcasts can be made anywhere within the band
88-108 MHz.
The
full mathematics of the AB effect has
been recently and elegantly been
developed by Bright et al (2015).
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1140/epjc/s10052-015-3670-8#
As
an alternative to water molecules as a receiver, DNA and whole cellular toroidal and caduceus
structures may act as receiving antennas
of electro-scalar waves. Ion channels too can display toroidal geometry. Analytical solutions of Poisson's equations
satisfying the Dirichlet boundary conditions for a toroidal dielectric boundary
are presented. The electric potential computed anywhere in the toroidal conduit
by the analytical method agrees with the value derived from an iterative
numerical method. Kuyucak (1998) show
that three different channel geometries, namely, bicone, catenary, and toroid,
give similar potential profiles as an ion traverses along their central axis.
They then examine the effects of dipoles in the toroidal channel wall on the
potential profile of ions passing through the channel. The presence of dipoles
eliminates the barrier for one polarity of ion, while raising the barrier for
ions of the opposite polarity. They also examine how a uniform electric field
from an external source is affected by the protein boundary and a mobile
charge. The channel distorts the field, reducing it in the vestibules, and
enhancing it in the constricted segment. The presence of an ion in one
vestibule effectively excludes ions of the same polarity from that vestibule
but has little effect in the other vestibule. Finally, they discuss how the
solutions we provide here may be utilized to simulate a system containing a
channel and many interacting ions. Toroidal
cell membranes are occasionally observed, e.g., in specialized structures of
plant cells like the prolamellar body,
see ‘From sphere to torus: a topological view of the metazoan body plan’
( Jockusch and Dress 2003).
Scalar
field radio emission as distinct from transverse wave was first predicted by
Nikola Tesla. Some recent experiment
shows positive results that are in qualitative agreement with the presented
predictions of scalar field effects, but further quantitative tests are
required in order to verify or falsify the presented theory. The importance of
Nikola Tesla's pioneering research, with respect to the predicted effects,
cannot be overstated, see van Vlaenderen (2003). Experimental
Scalar radio signals have been sent which penetrate a Faraday screen
using caduceus coils and toroid
https://www.google.com/patents/US5845220, see also Froning
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1875389211005773,
works by considering theory of Marengo (2002).
Not
only do biological systems and their structures from DNA to whole cells and
sub-cellular structures have suitable scalar wave antennas, they also have Bose
-Einstein condensates, see Frolich (ref) and more latterly Geesink and Meijner
(refs). An ideal scalar (information)
receiver is an AC Josephson junction. It
has recently been shown that a Bose Einstein condensate behaves as such. The possibility of AC Josephson Junctions
in biology was first discussed almost four decades ago by Achimowicz (1982). Only now is the realisation.
Using
the notion of scalar wave information, I have shown it is possible to separate
out the biological effects of radio waves in the far field even those
originating from multi-frequency transmitting sites. One simply seeks the distance or time delay
which represents a 180º or pi/2 phase difference at each given frequency and then
explores the distribution of cancers in radial locations defined by the given
distance and frequency. The same can
also be done for odd integer (n) multiples of this distance. Biological effects can sometimes be seen out to n=5 or even n=7. Antenna main beam and secondary side lobe
interactions (SSL) can produce e-field fluctuations at distances similar to but
not equal to those predicted by the quantum model advanced here. For instance
re-evaluation of the famous Sutro transmitter study results gives better fits
to the recorded cancer epidemiology according to the quantum model than it does
to SSL.
Indeed,
the very fact that this technique works at all and works well is a testimony as
to the correctness of Frolich’s
original assertions of coherence in biology as recently and elegantly expanded
upon by Geesink and Meijer.
Experimental
A
number of experimental sites were chosen on the basis of known association with
various cancers. Some of these were
associated with the demise of personal friends and even family members and
others were more anecdotally related or as a result of investigative work
following press reports. Site -finder
was used initially to find the locations of nearby transmitters and since its
closure more recently mast data dot com https://mastdata.com/. Where it was physically possible to visit
premises the expected RF spectra were confirmed using a hand-held spectrum
analyser see www.rf-explorer.com and RF field strengths were measured using
Cornet Microsystems ED88T 100MHz-8GHz tri-field meter. In all cases
distances between the site and
nearby transmitter masts were calculated using an on-line postcode distance
calculator.
Only
frequencies which fulfilled the necessary phase distance condition were
tabulated.
I have previously discussed what I have termed
‘RF’ cancers on the basis of their association with the inception of TV
Broadcasting http://www.drchrisbarnes.co.uk/Meta.htmla
and with RF fields at certain
locations. http://www.drchrisbarnes.co.uk/CancerHouses.htm.
A
number of individual cases are discussed in terms of my quantum mechanical
location model are to be found at http://drchrisbarnes.co.uk/More%20egg%20than%20chicken.html.
On
the basis of the proposed quantum mechanical far field interaction it is possible to identify which cancers are
associated with various transmission
frequencies by only considering cases
which satisfy the necessary phase
distance equation for each given
frequency as explained
above.
The
results of the pilot study are shown in Table 2 below.
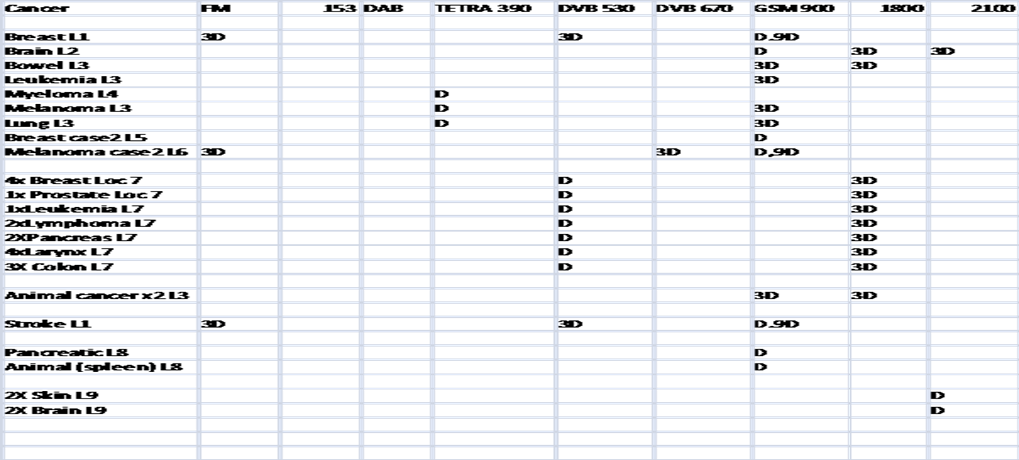
Table 2.
Analysis of results and Discussion
Far
field conditions are confirmed. The
nearest point of approach to a transmitting antenna in the results is condition
‘D’ at 2100 MHz which represents a distance of 238 m.
The
largest distance of possible interaction identified is 3D FM which is circa 15
Km.
To
be considered far field a signal needs
to be interacting at least two wavelengths from an antenna. This is 28 cm at 2100 MHz and 6m at FM.
Hence,
we can see the interaction is well in the far field.
In
Part 1 of the study the link established by others for GSM with regard to
glioma and prostate cancer was confirmed and also strongly supported the
present hypothesis of soliton/ion channel interaction. Amongst the so called ‘RF cancers I have
previously discussed, I established my own link between breast and prostate
cancer. If the same modes of
interaction are relevant in the far field
I would expect integer and odd integer quantum phase relationships as
explained above for GSM and any frequencies which reduce to the same on the
Geesink scale.
There
are 31 cases of human cancer and 3 cases of animal cancer and 1 young age stoke
in this pilot sample.
There
are 6 cases of breast cancer and at first sight the most common frequencies
appear to be DVB 530 MHz. However, it
should be borne in mind that two of these cases also fulfils the correct phase
relationship for GSM 900 and the other four for GSM 1800. In this respect it should be noted that all
have common modulation frequencies and that bot reduce to the same places on
the Geesink scale. In reality then it
would appear to be GSM that is the true
common denominator for breast cancer.
There
are 5 cases of haemopoietic cancers some with apparent involvement of GSM some
with DVB but no consistent theme.
There are 4 cases of
colon cancer GSM being the common denominator three of which also associated
with DVB 570 MHz . I have previously shown colon cancer to be
correlated as an ‘RF’ cancer.
There
are 3 cases of brain cancer and all are related to 2100 MHz UMTS. The structure
of a WCDMA signal is very complex and can be 1.5 or 5 MHz channel widths with
modulation components including 800 and 1500Hz.
The fundamental frequency reduces to 250 Hz on the Geesink scale. The modulation frequencies reduce to
375 and 400 Hz on the Geesink scale. 250
Hz has the potential to interfere with voltage gated sodium channels. Geesink has recently commented on a
bandwidth effect in bio-destabilisation.
The W-CDMA channel has far more bandwidth than GSM so possibly more
potency to promote glioma? 375 Hz
relates to either
magnesium or calcium channels and 400 Hz to hydrated proton channels.
There
is one case of lung cancer with a possible association with GSM or Tetra.
There
are 3 cases of Melanoma skin cancer but only one associated with FM as has been
suggested a possibility by Halberg and Johansson.
There
is 1 case of Prostate cancer seemingly associated with GSM. This is as would be
expected from the near-field study.
There
are 4 cases of Larynx cancer either potentially associated with GSM or DVB 530
or both.
There
are 3 cases of animal cancer, 1 dog lymphoma, 1 cat colon and 1 dog spleen all
potentially associated with GSM.
There
is 1 Pancreatic cancer, potentially associated with GSM 900MHz.
There is one case of young age stroke at a
the location exposed to the most frequencies which fulfil the quantum phase
relationship, incidentally this was also the location of a terminal case of
triple negative breast cancer.
No
further frequency division analysis needs to be done for the GSM cases since
the carrier and modulation frequencies are the same as those for the near field
study. However, in order to complete the analysis it is still necessary to check
the effects of any other frequencies which satisfy the quantum interaction
phase relationship and check which ion channels are involved.
In
the UK as a whole one might expect roughly equal probabilities of breast and
prostate cancer, but this is not borne out here. However, the sample size is
very small.
Voltage-gated
Na+ channels (VGSC) have been implicated in the metastatic potential
of human breast, prostate, and lung cancer cells. Specifically, the SCN5A
gene encoding the VGSC isotype Nav1.5 has been defined as a key
driver of human cancer cell invasion. Voltage-gated Na+
channel SCN5A is a key regulator of a gene transcriptional network that
controls colon cancer invasion, see House et al 2010.
Re-
consider a 900 or 1800 MHz GSM signal.
The carrier frequency reduces 429.15 Hz on the Geesink acoustic
scale. There are major modulation components at 217 Hz and 8.3 Hz.
It is known that harmonics of IPR frequencies also stimulate IPR. When these
are multiplied up appropriately they fall at 434Hz and 265.6 Hz on the same
scale. These modulation frequencies are
capable of soliton/ion channel interaction, in particular for voltage gated
sodium channels.
There
is thus support for the notion that human breast, prostate, colon and lung cancer
could all be initiated or promoted by RFR in the far field at either 900 or
1800 MHz with GSM modulation. Somewhat
surprisingly and contrary to the near field study no evidence of GSM
association with glioma at a distance was found. On the other hand 2100 MHz W-CDMA is
associated with glioma. Calculation
shows its fundamental frequency to disturb sodium channels. The apparent preference may simply be a
facet of small sample size. However, WCDMA is a very wide bandwidth
transmission and Geesink has remarked about the destabilising effects of such
bandwidth.
Unexpected
possible associations of GSM with larynx
and pancreatic cancer are suggested. DVB 530 MHz also reduces to 252 Hz on the
Geesink scale. These can only be
regarded as possibilities because the sample size is so small. Nevertheless it is instructive to check for
ion channel involvement. An extensive
literature search shows no reference to the expression of such channels in
these two cancers. I am forced
therefore to assume that larynx and pancreatic cancers are not in any way
associated with RFR. Larynx cancers
have known and strong associations with other factors such as smoking and
HPV. Tobacco and Obesity and heavy alcohol use are strong risk factors
for Pancreatic cancer. Pancreatic
cancer has also been associated with exposure to various pesticides.
There
is insufficient data to comment on the cases of individual Haemopoietic cancer
observed which simply leaves the melanomas.
However taken as a group the result for Haemopoietic cancers is
interesting. A 530 MHz DVB carrier can
have a modulation bandwidth of 8 MHz. at
the low end of the scale this corresponds with the voltage gated proton channel
Hv1 and is thus consistent with the Radio Ham near field study.
There are
no significant literature references to voltage gate Sodium ion channels
being relevant to Melanoma. According to
Hallberg and Johansson FM radio emissions are a causative factor in
melanoma. However the centre of the FM
broadcast band reduces to 335.4 Hz on the Geesing scale which they would view
as a ‘life stabilising
frequency’. A note of caution is
required, however, since there are multiple stations broadcasting at similar
power levels within the bandwidth giving the effect of a potentially 20 MHz
wide information carrier. Following Geesink and Meijner such a scenario would behave as highly
destabilising. Examination of the ion
channels which could be perturbed are the potassium channel and the magnesium/calcium channel. Some cases of Melanoma have been seen
associated with DVB 670 MHz and with TETRA 390 MHz. These reduce to 313 HZ( Potassium) and 374 Hz
(Magnesium) on the Gessink scale both in life destabilising bands. There are 2 skin cancers associated with
2100 WCDMA. The modulation frequencies
provide 300 and 400 Hz when reduced to the Geesink scale. 300 Hz can stimulate the potassium channel.
I
must enquire, therefore, if voltage
gated potassium and magnesium channels are involved in Melanoma and especially
if pharmaceutical blocking of such
channels inhibits the disease. Such a finding would strongly reinforce the
present hypothesis.
Silencing
the KCNK9 potassium channel (TASK-3) gene disturbs mitochondrial function,
causes mitochondrial depolarization, and induces apoptosis of human melanoma
cells, see Nagy et al (2014). There is
some limited reference to the involvement of the TRPM gene family of magnesium
channels
TRPM7 can be a protector and detoxifier in
both melanocytes and melanoma cells. TRPM8 can mediate agonist‐induced
melanoma cell death. Therefore, we propose that TRPM1, TRPM2, TRPM7 and TRPM8
play crucial roles in melanocyte physiology and melanoma oncology and are
excellent diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets, see Guo et al 2012.
It
would seem thus that RFR stimulation of either
voltage gated potassium and
magnesium channels is suggested and supports the hypothesis as drafted.
The
results for the fields study have been summarised in table 3
below.
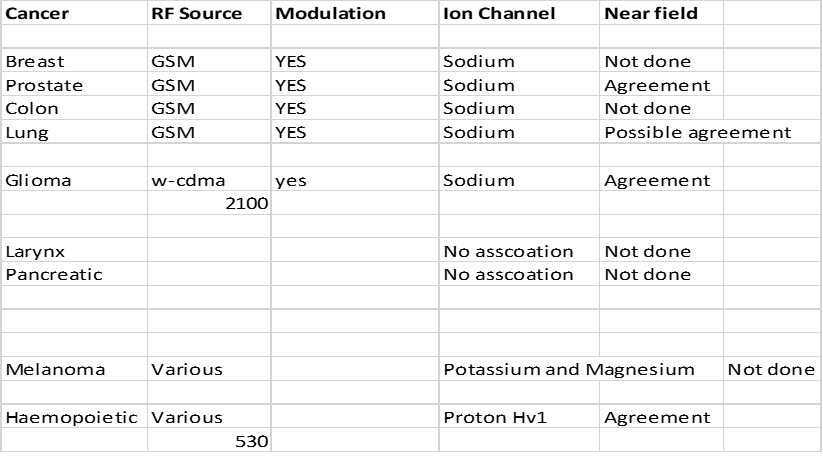
Table 3.
Discussion of Results
The
results of the far field study support the observation made by others that
different RF frequencies and/or modulation schemes are capable of initiating or
promoting different cancers.
The
results of both studies support the hypothesis of the author the RFR increases
activity in the over-expressed ion channels of cancers by means of soliton mode
/IPR coupling. Some cancers have more
than one over-expressed ion channel whereas ion channels are normally reserved
for excitable tissue. Even in the cases
of cancers with multiple overexpressed channels there is sufficient evidence in
the scientific literature to suggest that if a very specific type is pharmaceutically blocked proliferation
can be slowed or halted. RFR on a specific frequency seems to single out and
enhance this specific or ‘key player’ channel.
The
common denominator with the laboratory rodent study ( ref) and 21st
century RFR exposure is the it is all but continuous i.e. applied over the
entire cell cycle. Even with the
rodent study it was applied for 19 hours per day over the animal’s entire life
times.
The
near field study of Milham on Radio Amateurs may shed further light on the
matter. Radio Amateurs use many
different frequencies which ought to be capable of exciting many different
IPR’s and soliton modes and hence an excess of more than one type of cancer
ought to be expected. In fact this is NOT found to be the case and the data shows that hemopoietic cancers are the only ones found in this group
to excess. I have proposed here that
the 60 Hz fields form amateur power supplies etc. may be sufficient to cause
the observed excess. The Milham study
also shows that the group of radio amateurs as a whole had considerably and
statistically significantly less lung cancer than the public as a whole. It ascribed the reason as ‘higher’
socioeconomic class. My understanding
of radio amateurs is that the great majority are ordinary people, I wonder therefore, if short intermittent
exposure to certain RF frequencies is actually beneficial.
Analysis
of the common frequencies used by radio hams suggests that with the exception
of the 15 metre band most fall on the
Geesink 433 Hz condensate and would stimulate the chloride IPR. 15 metre band reduces to 324 Hz on the Geesink
condensate which would stimulate potassium IPR and TRPM7.
Intermittent
exposure to low level modulated RF has also recently been used as an
experimental treatment method for advanced hepatic carcinoma, see……
A
carrier frequency of 27.12 MHz was employed modulated by a number of amplitude
modulated frequencies, the so called TTF’s ( tumour treating frequencies)
applied in sequence.
This
carrier frequency reduces to 413 Hz on the Geesink scale close to the chloride
channel.
The
2,221.323 Hz TTF reduces to 277.63 Hz,
very close to the 278.9 Hz condensate/Ca2+
and Cl- (aq) IPR coherence.
10,454.4
Hz TTF Reduces to 326.7 condensate/ potassium channel and/or TRPM7.
6530.24
TTF
Reduces to 408.14 Hz close to but not on
either harmonic of hydronium ion or anhydrous chloride.
All
of the channels that seem to promote cancer as identified in this present study
are cation channels, NaV1. Etc, Hv1, Potassium and TRPM.
I
enquire therefore if RFR stimulation of anion channels specifically inhibits
cancer? I hypothesise that this is why
Radio Hams may have less lung cancer than the population at large? The common channel between Ham Radio
exposure and some of the TTF’s above is the
chloride channel. The paradox is
I have previously shown the dangers and genotoxic aspects of the chloride
channel. (REF).
I
hypothesise that the effects of RFR
on the chloride channel are duty cycle specific. In the world at large RF emissions are
continuous. However, in the amateur
radio shack RF emissions are highly
intermittent.
The
cell cycle times for malignant cells are very short and mitosis continues
unchecked. Normal cells have long cell cycles.
I suspect the short bursts of RF from Ham radio signals and TTF
frequencies interfere effectively with the cell’s cycle.
I
enquire if there is evidence in the literature that an upregulated chloride
channel can be used for cancer treatment.
The work of Okada et al (2006) confirms my argument exactly.
According
to Okada et al, apoptosis is an essential process in organ development, tissue
homeostasis, somatic cell turnover, and the pathogenesis of degenerative
diseases. Apoptotic cell death occurs in response to a variety of stimuli in
physiological and pathological circumstances. Efflux of K+ and Cl− leads
to apoptotic volume decrease (AVD) of the cell. Both mitochondrion-mediated
intrinsic, and death receptor-mediated extrinsic, apoptotic stimuli have been
reported to rapidly activate Cl− conductances in a large variety of cell types.
In
epithelial cells and cardiomyocytes, the AVD-inducing anion channel was
recently determined to be the volume-sensitive outwardly rectifying (VSOR)
Cl− channel which is usually activated by swelling under non-apoptotic
conditions. Blocking the VSOR Cl− channel prevented cell death in not
only epithelial and cardiac cells, but also other cell types, by inhibiting the
induction of AVD and subsequent apoptotic events. Ischemia-reperfusion-induced
apoptotic death in cardiomyocytes and brain neurons was also prevented by
Cl− channel blockers. Furthermore,
cancer cell apoptosis induced by the anti-cancer drug cisplatin was recently
found to be associated with augmented activity of the VSOR Cl− channel
and to be inhibited by a Cl− channel blocker. The apoptosis-inducing VSOR
Cl− channel is distinct from ClC-3 and its molecular identity remains to
be determined.
Min
et al (2011) have obtained results which suggest that impaired activity of VSOR
Cl− channels contributes to the cisplatin resistance in A549/CDDP cells.
Bustin
et al have showed that certain classes of chloride channel gene are down regulated in some cancers. Their results
suggest that CLCA1 could specify a new tumour suppressor and that, as in breast
cancer, CLCA2 may function as a tumour suppressor in colorectal cancer, see Stephen A. Bustin, Shu-Rui Li, and Sina
Dorudi.DNA and Cell Biology. Jun 2001.ahead of
printhttp://doi.org/10.1089/10445490152122442
The
behaviour of some chloride channels is a double-edged sword. See Suh et al, 2005.They find that chloride intracellular channel (CLIC)4
is a p53- and tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα)-regulated chloride
channel protein that is localized to the mitochondria and cytoplasm of mouse
and human keratinocytes. CLIC4 protein increases in differentiating
keratinocytes and in keratinocytes exposed to DNA-damaging agents and metabolic
inhibitors. Increasing CLIC4 levels by transduction of recombinant CLIC4 causes
apoptosis. CLIC4 translocates to the nucleus under a variety of conditions of
cell stress, and nuclear CLIC4 is associated with cell cycle arrest and
accelerated apoptosis. Yet reduction of
CLIC4 and several other CLIC family members by expressing a
doxycycline-regulated CLIC4 antisense also causes apoptosis in squamous cancer
cell lines.
Again
I suspect both loss of p53 and cell cycle times are involved in the latter
case.
Conclusions and further work.
A
new hypothesis to explain the observation of different cancers being associated
with different frequencies and modulations in a recent very large rodent near
field RFR/cancer study ( ref) has been developed and fully supported,. There is considerable support also when the
model is extended to the far field and linked with the authors quantum
mechanical frequency distance interaction model to be expected when dealing
with soliton modes.
The
hypothesis that RFR stimulation of cation IPR/soliton modes is either cancer
causing or cancer promoting is supported.
Different cation modes are associated with different cancers.
The
hypothesis that RFR stimulation of certain voltage gated chloride channels and
their associated soliton modes may be anticancer, especially for lung cancer,
and especially when applied for transient periods is also supported.
The
IPR ion/ soliton model of interaction too justifies further investigation. RF and DC field can predict the IPR frequency
but there is no reason to suppose that the soliton mode in itself does not set
the genetic expression of or
shape and size of the
channel.
The
work on ion channels is essentially a beginning, perhaps an
oversimplification. This is hardly
surprising given that many ion channels encoding genes have
‘superfamilies’(ref). No fewer than 10
genes encode for sodium, 16 for
potassium and a staggering 100 for potassium.
This probably explains the observation of common and personal tumour
treating frequencies as mentioned by
Zimmermann et al (20120> https://www.nature.com/articles/bjc2011523
There
is scope for considerable further work which could potentially be of immense
benefit to human kind.
1. I
propose getting cancer registries to release as much data as possible to be
used with a GIS study to fully validate both the quantum and IPR/soliton
hypotheses.
2. I
propose that extensive laboratory studies are needed to look into RF and
modulation duty cycle effects on the various phases of healthy and cancer cell
cycles.
Only
with such data can we fully understand this enthralling subject and develop a
truly electromagnetic and drug free cancer medicine regime.